Facilitator(s)
- Chaya R. Jain, Professor, Virginia State University
- Tristan T. Utschig, Associate Director for Learning Sciences, Kennesaw State University and Associate Professor of Nuclear Engineering
Why?
Practicing two of the most salient aspects of teaching — reflection and assessment — can produce incredible efficiency for instructors seeking to improve student learning.
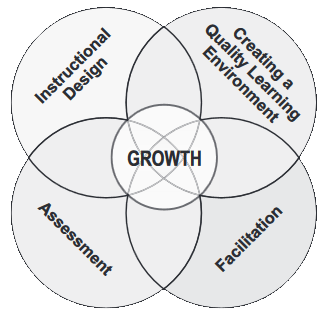
Learning Objectives
- Participants will learn to incorporate the four pillars
of PE supporting student growth in the reflection and
assessment of teaching:
- Creating a Quality Learning Environment
- Instructional Design
- Facilitation
- Assessment
- Participants will explore factors within the proposed model that may be of particular interest to educators having culturally diverse learners.
Performance Criteria
- Participants will offer their team an example to consider in addressing at least one student learning constraint they encountered during their classroom teaching experience.
- Teams will specifically incorporate content from the IJPE article and two FGB modules in a reflection report and an assessment report.
- Each participant will contribute one or more ideas included in team reflection and assessment reports recorded on the session worksheet.
Resources
- IJPE article: Leveraging Elements of Process Education to Extend Biggs’ Model of Constructive Alignment for Increasing Learner Achievement (be sure to at least read the abstract)
- IJPE article: A Comparative Analysis of Reflection and Self-Assessment
- PowerPoint summary of a PE study on collaborative learning
- FGB module: Methodology for Creating a Quality Learning Environment
- FGB module: Overview of Facilitation
- Forum for this workshop: http://www.processeducation.org/moo/mod/forum/view.php?id=14
- Session Worksheet
Glossary
- Assessment
- Reflection
- Facilitation
- Learning environment
- Instructional design
- Culturally diverse learners
A process of determining the quality of a performance, work product, or skill and giving feedback that documents progress (strengths) and suggests ways to improve future performance (areas for improvement) in ways that will help the performer improve his or her future performance
Reflection is a process that involves playing back a period of time related to previous valued experiences in search of significant discoveries or insights about oneself, one’s behaviors, one’s values, or knowledge gained. Specific criteria for performance are usually not involved. An important goal in reflection is bringing focus to an indeterminate situation (Dewey, 1938) by gaining clarity and by fully experiencing what has happened. It is important to gain closure during reflection and not ruminate repeatedly about the experience. Reflection involves divergent thinking and often includes journaling.
Actions taken to help others learn or perform. In a learner-centered paradigm, facilitation takes the place of teaching, stressing the centrality of the learner’s work in the learning process.
Learning environment refers to the diverse physical locations, contexts, and cultures in which students learn. Since students may learn in a wide variety of settings, such as outside-of-school locations and outdoor environments, the term is often used as a more accurate or preferred alternative to classroom, which has more limited and traditional connotations—a room with rows of desks and a chalkboard, for example.
Instructional design is the determination and specification of the content, methodologies, activities, sequencing, evaluation, and assessment of the learning experience. The process of instructional design follows an iterative cycle which analyzes what the learner is to learn, designs and develops learning events to activate learning, implements the design, and assesses the process that leads to constant improvement of the instructional design.
Students who present with an ethnicity, race, socioeconomic status, gender, learning modality, cognitive development, and/or social development that differs from the predominant
Plan
- Overview of session plan
- Assessment and Reflection overview: Using the IJPE article on assessment and reflection, teams create a brief statement of what an assessment and reflection report might each include when applied to a specific PE context.
-
Case study of reflection and assessment applied to a
collaborative learning instructional intervention
- Brief summary of an example PE study by session facilitators
- Question and answer period on the techniques to conduct
- reflection, which involves: (a) consideration of learner constraints within the learning environment; (b) consideration of student learning outcomes as related to the ‘learning to learn’ process; and (c) reflection on processes underlying student growth.
- Next, a systematic assessment of the overall intervention process using PE’s assessment methodology of Strength, Improvement and Insight (SII) method.
- Applying reflection and assessment techniques to a
learning constraint experienced by a team member
- Teams choose one learning constraint a member of the team is facing
- Reflection – on their worksheet, teams produce a reflection report related to this learning constraint for that team member
- Assessment – on their worksheet, teams produce an assessment report related to this learning constraint or that team member
Critical Thinking Questions
Answer these on the forum for this worksohp: http://www.processeducation.org/moo/mod/forum/view.php?id=14
- What is reflection?
- What is assessment?
- What is the added value from doing both of these two processes?
- How can assessment and reflection be made to specifically address different situational teaching and learning contexts?
Exercise
- In teams: participants may share one learning constraint they encountered during their classroom experience for discussion within their team and “resolution” using reflection and assessment tools.
- Teams should produce a reflection report that addresses the learning constraint your team selected. (Post reports to the forum for this workshop: http://www.processeducation.org/moo/mod/forum/view.php?id=14)
- Teams should produce an assessment report that addresses the learning constraint your team selected. (Post reports to the forum for this workshop: http://www.processeducation.org/moo/mod/forum/view.php?id=14)
Closure
Teams each report on 1-3 concepts/ideas/insights gained about assessment and reflection (as applied to improving teaching and learning) during the session